Coated CBN tools for machining Aube ductile iron
2023-06-08Austempered Ductile Iron (ADI) is a ductile iron with an austenitic and bainitic matrix obtained by isothermal quenching, also known as Austempered Ductile Iron. Combining high strength bainite and spheroidal graphite, ADI has excellent overall properties such as high specific strength, wear and abrasion resistance, sound absorption and vibration damping, good notch sensitivity, impact toughness and fatigue strength, while retaining the benefits of the original casting process and allowing the manufacture of complex shaped parts. Compared to similar materials such as cast steel and cast aluminium, it has optimum economic performance.
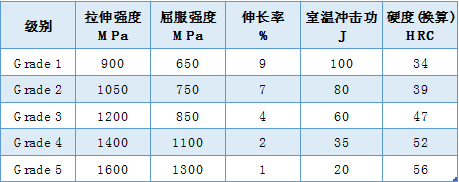
American Standard ASTM A897/A897M-2015
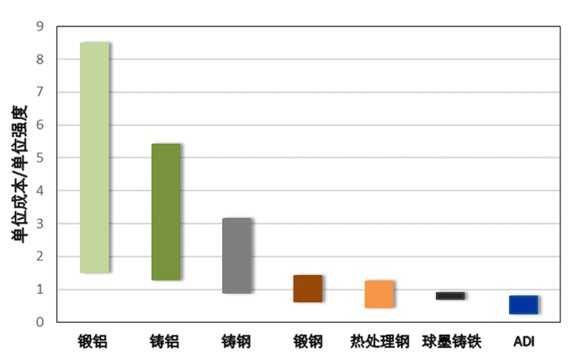
Comparison of the relative economics of different materials
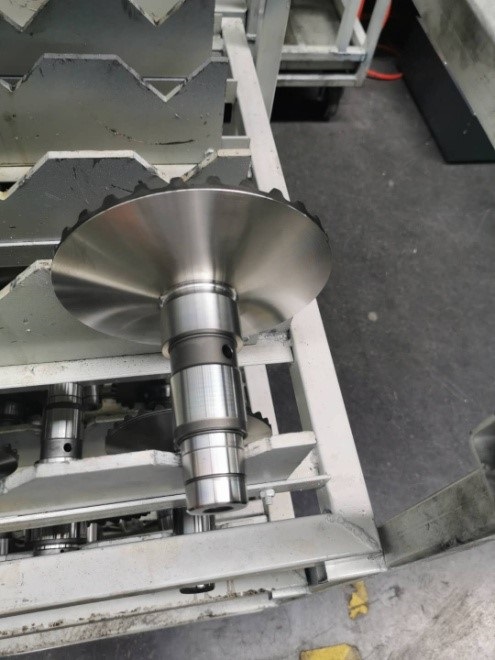
After entering the 21st century, the application of isothermal quenched ductile iron in the automotive, engineering machinery, shipbuilding heavy industry, agricultural machinery, metallurgy and mining, wind power, high-speed railway parts and other industries is developing rapidly. For example, gears, crankshafts, camshafts, transmission output shafts, suspension control arms, isothermal universal joints, engine mounts, tow hooks, brake tripods, transverse stabilizer bars, suspension brackets, wheel hubs, clutch release bearing sleeves, suspension spring seats, differential cross shafts, and marine engine cylinder liners, etc. for light, medium and heavy trucks.

Tuscan Speed 6 sports car Orbe ductile iron crankshaft

Cylinder liners for heavy propagation ships' engines
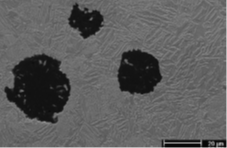
Scanning electron microscope photograph of ADI microstructure.
Among them, spherical graphite accounts for about 15% of the volume ratio of the material.
The spherical graphite has an average diameter of 30μm and an average pitch of 75μm
● Similarly to normal ductile iron, during the mechanical machining of ADI, the ferroalloy matrix and spheroidal graphite have very different strengths, corresponding to intermittent cutting with high tool vibration, which can easily cause chipping.
● At the same time, for isothermal quenching heat treatment phase diagram and process considerations, ADI in the composition of the austenite forming elements such as nickel (Ni 0.73wt%), copper (Cu 0.87wt%) content, as well as play a strengthening and antioxidant effect of the molybdenum element, chip sticking tool serious, increasing the rapid wear of the tool.
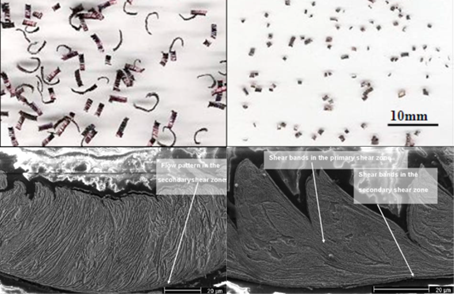
PCBN machining Grade 4 ADI, chip macrophotograph and SEM morphology.
Left, cutting rate Vc=100 m/min;
On the right, Vc = 400 m/min.
(Feed f = 0.05 mm/rev, depth of cut 0.2 mm)
As the cutting speed increases from 50m/min to 200m/min, chip deformation hardening plays a leading role and the hardness of the chip and the main cutting force increases. As the cutting speed continues to increase, the chip gradually changes from ribbon-like to serrated, the chip breaking effect is gradually accentuated and the cutting force is gradually stabilised. Cutting speed exceeds 400m/min, cutting deformation and cutting temperature increase induces martensitic phase change of residual austenite in the microstructure of ADI, the hardness of the chip increases and accelerates the acceleration of PCBN inserts. Continuing to increase the cutting speed, the chip undergoes tissue recovery and oxidation at high temperatures, and insert wear increases.
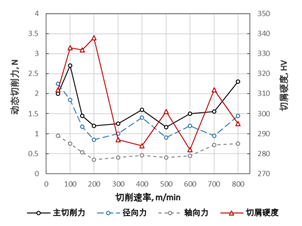
PCBN machining Grade 4 ADI, cutting forces and chip hardness vary with cutting speed.
For the above mentioned problems in isothermal hardened ductile iron machining, internationally and nationally known tool companies lack effective solutions. In general, considering the chipping of interrupted cuts, priority is given to PCBN materials with a medium CBN content (65%, 70%, up to 75%), preferably with a metal-like bond (titanium alloy or Al/Ni/Co). A suitable coating, meanwhile, is an effective means of improving the effectiveness of PCBN machining ADI.
WSS Precision Tools (Shanghai) Co., Ltd. has developed a composite nano-functional coating (patented as a national invention) that combines the bonding, anti-wear and anti-adhesion properties of PVD film with initial success in trial cutting of hardened steel. Together with our previous successful experience in processing ductile iron, it is expected to become a powerful tool for isothermal hardening of ductile iron.



